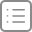
随着越来越多的膜表面受体被纯化,其结构及转导信号的方式逐步得以阐明。目前,按照受体的结构及其作用方式可将其分为三大类。这三大类受体在配体种类、受体的一般结构和功能及细胞对之发生反应的方式上有所不同,见表21-2。
Table 21-2 Classification of MembraneReceptors:Characteristics of Three Groups of Receptors
| Characteristics | Ion Channel Receptors | G-Protein-Linked receptors | Recetpors with a Single Transmembrane Domain |
| Endogenous ligands | Neurotransmitter | Neurotransmitter | Growth factor hormone |
| Hormone | Cytokine | ||
| Auloacoid | |||
| Chemotactic factor | |||
| Exogenous stimulant | |||
| Structure | Oligomer with a pore | Probably monomer | Monomer of oligoner |
| with (±)catalytic | |||
| domain | |||
| Number of transmem | Four per subunit | Seven | One per subunit |
| bane segments | |||
| Function | Ion channel | Activation of G proteins | Tyrosine kinase |
| Giuanylate cyclase(?) | |||
| Cellular responses | Depolarization or | Depolarization or | Regulation of function |
| hyperpolarization | hyperpolarization | and expression of | |
| Regulation of function | proteins | ||
| and expression of | Proliferation or | ||
| proteins | differentiation |